Forex Options Trading – Understand Calls & Puts for Currencies
| Position | Company Logo | Information | Bonuses | Min. Dep | Regulation | Open an account |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $20 |  |
||
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
4
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
5
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
||
|
6
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $5 |  |
||
|
7
|
 |
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
|
|
8
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
9
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
10
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
|
|
11
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
||
|
12
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $25 |  |
|
|
13
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
|
|
14
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
||
|
15
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
|
|
16
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $2 |  |
|
|
17
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $500 |  |
The trading community doesn’t talk much about Forex options trading. However, it is a very rewarding way to profit from the foreign exchange market. Option trading allows traders to speculate on currency pairs without taking ownership of the actual currencies. It gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified date.
In this guide, we share information about options Forex trading, including the different types and practical examples of how to trade.
What is a Currency Option?
A currency option, also known as a Forex option, is a derivative financial instrument that gives the owner the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a specific currency pair at a specified exchange rate on or before the expiration date. The buyer of a currency option pays a premium to the seller for this right. The seller then carries the corresponding obligation to fulfill the transaction if the buyer chooses to exercise the option.
The Basics Concepts in Forex Options Trading
There are a few key terms to understand when trading currency options :
- Premium: The upfront sum that the option buyer pays the seller. It represents the maximum risk for the buyer.
- Strike price: The price at which the holder can buy or sell the underlying currency pair if they exercise the option.
- Expiration date: The last day the option can be exercised.
- In the money: when the strike price is below the market price for calls or above the market price for puts.
- Out of the money: when the strike price is above the market price for calls or below the market price for puts.
Currency options are traded over-the-counter (OTC). Quotes are presented as bid/ask spreads rather than a single price. The spot exchange rate, volatility, currency interest rates, and time until expiration all have an impact on option prices.
How Forex Options Trading Works
One key difference between options and spot forex is options only deliver the actual currency at defined expirations, rather than direct ownership like spot. They also have set quarterly expiration cycles unlike continuous 24/7 spot trading. Like with other types of trading, there are two sides to options trading: buying and selling.
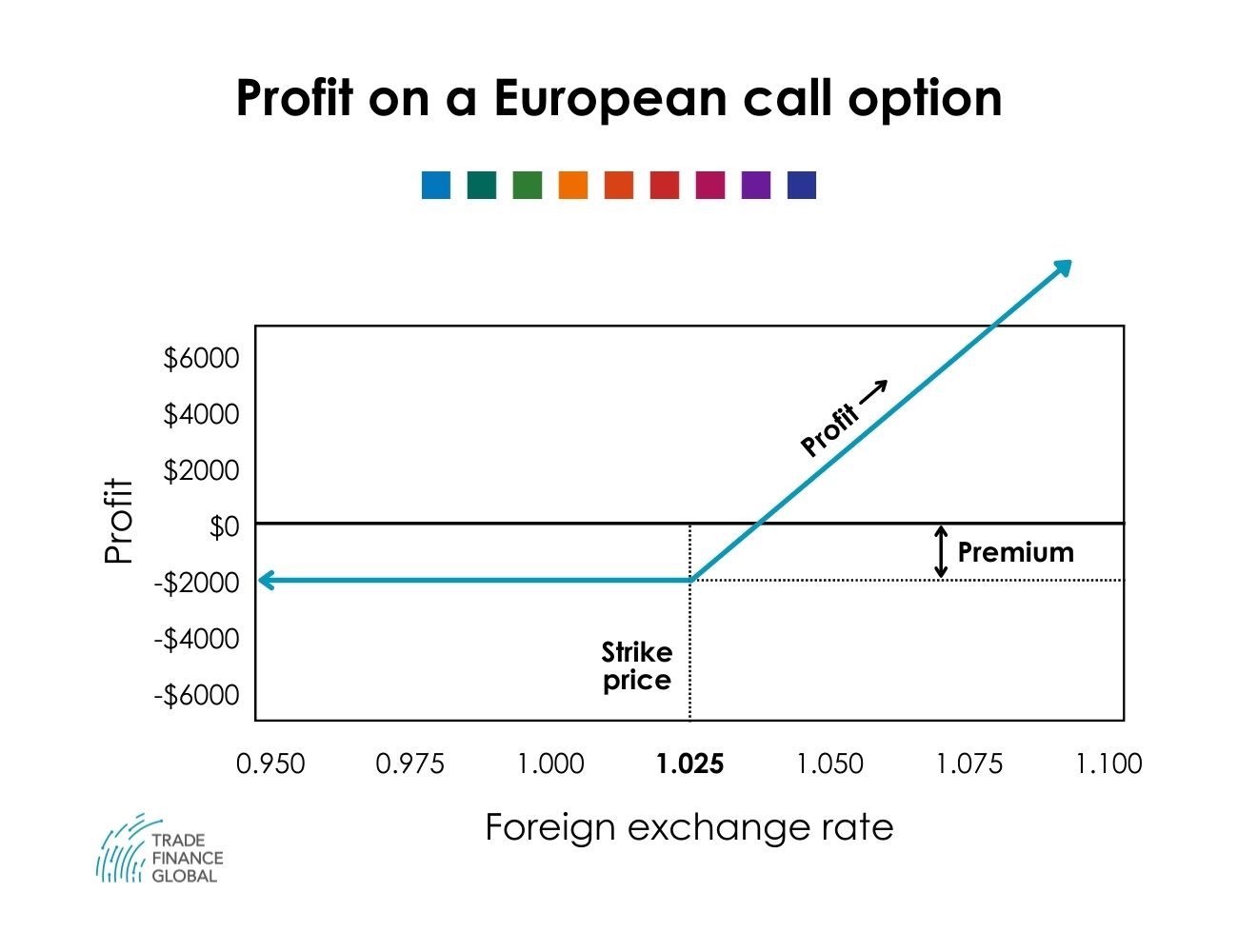
Long Call/Put
The buyer of a call or put option pays an upfront premium to control the right, but not obligation, to transact in the underlying currency pair at the specified strike price any time until expiration. For example, long a EUR/USD 1.1500 call option allows buying euros at 1.1500 before expiry.
Prior to option expiration, long holders can sell back contracts to the market to close rather than exercising for the currency itself.

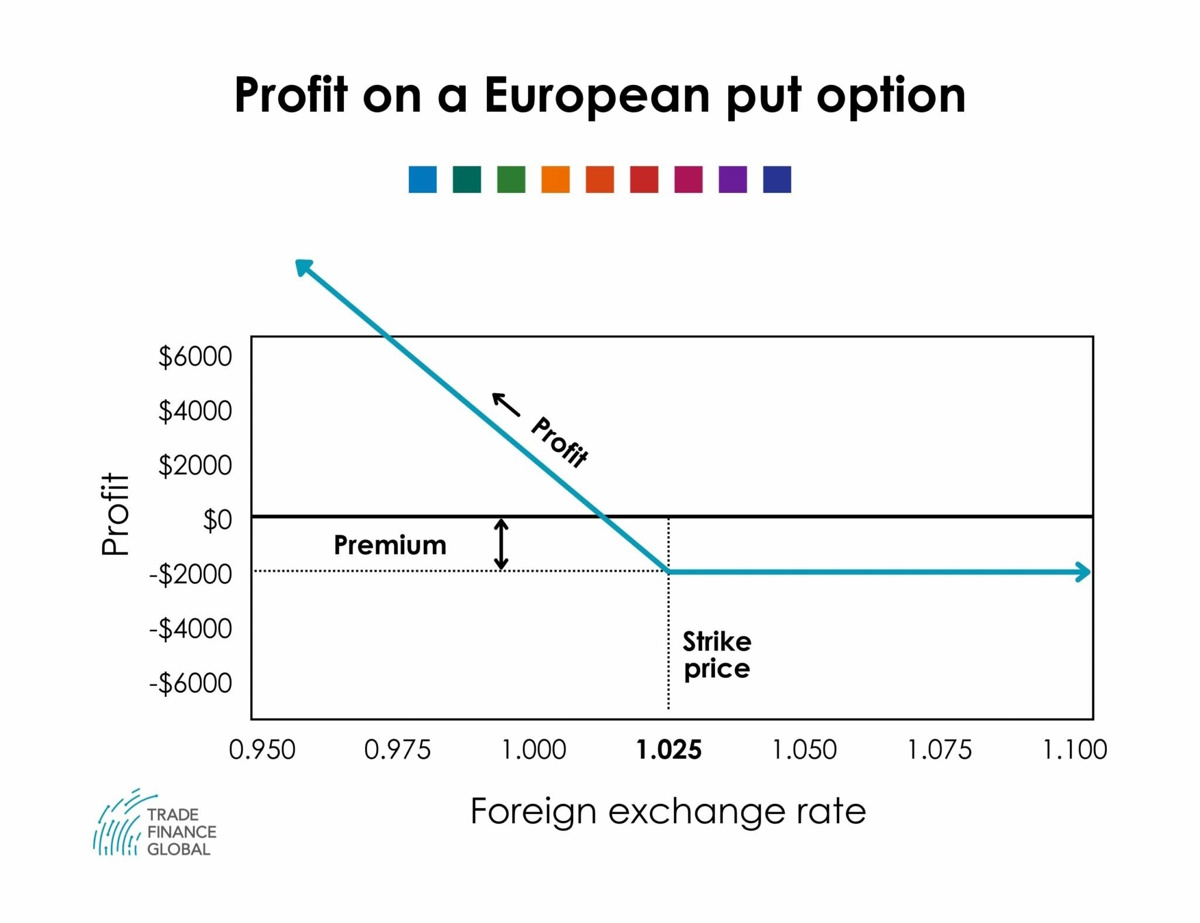
Short Call/Put
The seller of options takes in the premium income upfront but has uncapped loss exposure if the underlying moves severely against their position at expiration. For instance, short a EUR/USD 1.1500 call obligates selling euros at 1.1500 to the long call owner if that options gets exercised while the euro is higher.
Equally, short sellers can buy back the options they wrote to cap losses if the currency pair moves against their short contracts.
Types Of Forex Option Trading
There are basically two types of Forex options trading: vanilla options trading and SPOT options trading. Let’s take a look at both to understand how they differ.
Vanilla Options Basics
Vanilla options are the basic calls and puts that make up most retail Forex option trading. This type of option gives the buyer potential for upside gains with limited downside risk. Since the buyer can choose whether to exercise the option, their loss is limited to the premium cost if the market moves against them.
On the other hand, the buyer enjoys uncapped profit potential if the currency pair moves favorably. These traits make vanilla options useful for speculating directionally without taking on full exposure to currency fluctuations.
In addition, vanilla options present opportunities to hedge existing currency risk exposure in an investment portfolio. For example, an investor with a large position in euros could buy EUR/USD put options to protect against potential declines versus the US dollar. The put options can offset losses on the broader portfolio if the euro drops as expected.
Vanilla options pricing depends on several key factors. These include:
- The moneyness, which is how far the strike price sits from the current market price,.
- The implied volatility of the currency pair also impacts option valuation; higher volatility raises the chances of a favorable price move.
- Relative interest rates between the currencies affect pricing as well.
- Time until option expiration plays a role too; more time allows a greater chance the currency rate reaches a level to profit.
Example of a Currency Option Trade
Here is an example of how currency options trading works:
Setup: The trader expects USD/JPY to rise over the next month from the current spot rate of 115.00. They buy a one-month USD/JPY call option with a 117.00 strike price for a premium cost of 30 pips.
At expiration, if USD/JPY rises to 118.00, it will increase the money by 100 pips. Intrinsic value is (118.00 – 117.00) x 100 = 100 USD profit. After subtracting the 30 pip premium cost, the trader’s net profit is 70 USD.
If USD/JPY drops below 117.00, you are out of money, and the call option expires worthless. The trader loses the 30-pip premium paid.
SPOT Options Basics
SPOT options, also known as digital or binary options, represent a unique form of currency option. They carry an all-or-nothing payout structure tied to whether a defined trigger event occurs before the SPOT option expires. Common triggers include the currency pair hitting a target price level at expiration.
One major benefit SPOT options provide is limited downside risk, capped at the premium amount paid to enter the trade. The payout potential is preset at a fixed amount if the option finishes in the money. This creates a binary-type payoff—the entire payout sum or nothing at all.
Once traders buy a SPOT option, no early exercise is allowed, and the contracts cannot be closed before expiration. Instead, the holders must wait for the customized trigger event to determine if a payout is achieved.
Example of Spot Forex Option Trading
Setup: The trader expects volatility in EUR/USD to rise over the next 5 minutes. They buy a EUR/USD SPOT call option that pays out 70% of the premium amount if EUR/USD closes above 1.1500 at expiration, which aligns with the trader’s volatility forecast. The current premium cost is $50.
At expiration:
If EUR/USD rises and closes at 1.1600, it is in the money as it finished above the 1.1500 trigger level. The SPOT call option pays out 70% x $50 = $35, giving you a balance of $85.
If EUR/USD drops and closes at 1.1400, it will be out of the money as it finished below the 1.1500 trigger. The SPOT call option expires worthless and the trader loses the $50 premium paid.
Benefits of Trading Forex Options
There are several advantages active traders seek when trading options compared to only trading currency spot contracts:
- Define and Limit Risk: Maximum loss is capped at the premium paid to enter an option trade, unlike straight spot positions with uncapped loss potential. Defined risk boosts position-sizing flexibility.
- Leverage: Options provide leverage, like margin trading, since less upfront capital is required to control large currency positions. Boost potential gains while capping downside risk.
- Hedge Spot Trades: Options help hedge an existing portfolio from adverse swings. For example, if there is a long EUR/USD spot, buy a EUR put to protect against a declining euro. Think of options as insurance to offset losses.
- Speculation and Directional Bets: No obligation to execute an option provides flexibility for traders to capitalize on or protect against short-term spot price swings. Useful for volatility spikes or key events.
Conclusion
Forex options trading deserves consideration for currency speculation and portfolio diversification. The limited downside risk makes them appealing for small account holders or risk-averse investors. Traders comfortable with technical chart analysis can use options to speculate on price trigger levels.
However, options involve defined profit potential and added upfront costs of premiums that spot currency trading avoids. Interested investors should learn more about options pricing and break-even calculations before jumping in. Proper education and strategy development are key to effectively using this leveraged product.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risks of trading Forex options?
The main risks are the outright loss of the premium paid, opportunity risk if prices surge higher, and early assignment if shorting options. Be aware of all possible outcomes before entering any trade. Only risk capital you can afford to lose.
Is it better to buy or sell currency options?
When starting out, it’s generally better to be an option buyer and define your maximum loss as the premium amount paid. Be careful shorting or writing options with unlimited loss potential; only experienced traders should do this.
How much can you make with Forex options trading?
Profits depend on the premium paid, strike price distance from the actual price at expiration, trading size, and payout multiplier for SPOT options. ROI rather than the raw profit amount determines success. Returns well over 100% per year are possible with savvy options trades.
Do you need a margin account for options trading?
Most Forex brokers require margin accounts as collateral for writing naked call or put options. For outright long option buying, some brokers allow cash accounts with no margin. Check broker policy specifics before trading any Forex derivatives like options or futures.
Which currency pairs have the most options trading volume?
The major pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CHF have excellent liquidity and daily option expirations available. Exotic pairs may only have monthly expirations, limiting flexibility. Stick to majors until you gain experience and account size.















