Forex Trading vs Stock Trading
| Position | Company Logo | Information | Bonuses | Min. Dep | Regulation | Open an account |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $20 |  |
||
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
 |
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
4
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
5
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
||
|
6
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $5 |  |
||
|
7
|
 |
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
|
|
8
|
|
|
Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
9
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $250 |  |
||
|
10
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
|
|
11
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
||
|
12
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $25 |  |
|
|
13
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $100 |  |
|
|
14
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
||
|
15
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $10 |  |
|
|
16
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $2 |  |
|
|
17
|
|
|
No deposit bonus | Minimum Deposit: $500 |  |
Forex trading and stock trading are two of the most popular forms of trading and investing. Both markets offer opportunities for traders to profit, but they have some key differences. This article provides an overview of forex and stock trading, compares the two markets, and discusses the correlation between them.
What is Forex Trading?
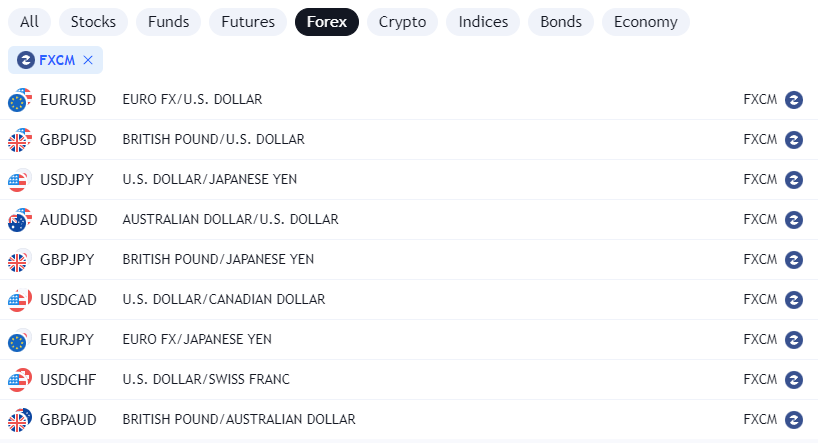
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global decentralized market for trading currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $ 7.5 trillion. The size of the forex market far exceeds that of the stock market.
In forex trading, participants buy and sell different currencies, betting on price movements. For example, a forex trader may sell British pounds in exchange for U.S. dollars if they expect the dollar to appreciate relative to the pound.
The main participants in the forex market are banks, hedge funds, commercial companies, investment management firms, and retail forex brokers and traders. Forex trading is all about buying and selling currencies in order to profit from favorable exchange rates.
Some of the major currencies traded include the U.S. dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese yen (JPY), British pound (GBP), Swiss franc (CHF), Canadian dollar (CAD), and Australian dollar (AUD). The most traded currency pair is EUR/USD.
Forex is a financial market that operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week across the globe. This enables traders to react to news and events that affect currency valuations day or night.
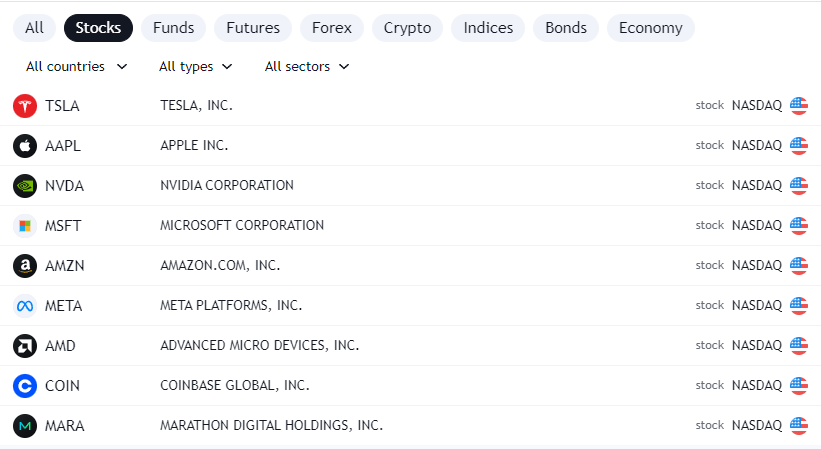
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies on stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange or Nasdaq. Stocks represent ownership in the company that issues them.
Stock traders aim to profit from price movements in the shares of companies. For example, a trader may buy Microsoft shares if they believe the stock price will increase over time. They can then sell the shares later for a higher price and pocket the difference.
The most commonly traded stocks are those issued by large, stable companies known as blue chips. Examples include Microsoft, Apple, Amazon, and other household names. Stock trading also includes smaller, more speculative companies.
Unlike the forex market, the stock market only operates during business hours on weekdays. Stocks can be volatile, but prices generally reflect longer-term valuations and trends in the underlying companies. Stock traders usually have a longer time horizon than forex traders.
Key Differences Between Forex and Stock Trading
While both forex and stocks offer trading opportunities, they have some notable differences. The main differences between the stock market and the forex market is shown below:
| Factor | Forex Trading | Stock Trading |
| Trading Volume | Over $7.5 trillion daily | $200 billion daily |
| Market Hours | 24 hours, 5 days a week | 9:30am to 4pm, weekdays |
| Volatility | High intraday volatility | Less volatile long-term |
| Leverage | High leverage up to 1:500 | Lower leverage requirements |
| Assets Traded | Currencies | Company shares |
| Participants | Banks, institutions | Broader individual participation |
| Analysis Tools | Technical analysis dominates | Fundamental analysis important |
| Trading Frequency | Very active intraday trading | Less frequent trading, long-term holds |
| Price Impact | Macroeconomic forces | Company performance, earnings |
| Correlation | Currencies correlated loosely | Stocks often trade in sync |
Trading Volume
The immense trading volume of over $7.5 trillion daily in the forex market, compared to $200 billion in the stock market, provides superior liquidity and ease of entering and exiting trades. The sheer number of participants makes forex more accessible. For example, a large $5 million position can be established instantly in the major EUR/USD currency pair, while such a position may be challenging to build in all but the most liquid mega-cap stocks.
Market Hours
Market hours also favor active forex traders, with the ability to trade 24 hours a day from Monday to Friday. Prices often gap higher or lower when markets reopen each day, allowing for potential profits. Meanwhile, stock traders are limited to exchange hours, unable to capitalize on news and events outside of market operating times. The nonstop nature of forex trading enables constant opportunities.
Volatility
While stock prices are generally less volatile than forex in the long run, forex volatility provides excitement in the short term. Currency values can fluctuate wildly intraday off economic data releases, central bank policy shifts, geopolitical events, and risk sentiment changes. Adaptive traders thrive on the sharp price swings. Stocks move too, but less explosively over months or years barring company specific events.
Leverage
The high leverage available in forex empowers traders to control $50,000 of a currency with just a $1,000 margin deposit in a 50:1 leverage account. This enables bigger position sizes with less capital. In contrast, margin requirements in equities limit leverage to 2:1 or less, necessitating more cash to establish equivalent sized stock positions. Forex’s extensive leverage presents opportunity along with amplified risk.
Diversity
While thousands of stocks exist, forex trading centers on just a few major currency pairs. This narrowed focus makes it simpler to analyze the forex market and track flows in eight or ten currency pairs rather than thousands of stocks. Fundamental factors like monetary policy and GDP growth largely drive currencies, while company specifics determine stock prices.
Assets Traded
The actual assets traded differ considerably between forex and stocks. Stocks represent ownership shares in individual publicly-traded companies, meaning their prices depend on company performance, earnings, products, leadership, and other microeconomic factors. Currencies, on the other hand, are macroeconomic assets whose values are driven by broad economic forces like interest rates, trade balances, inflation, political dynamics, and risk appetite.
Participants
Lastly, banks and institutions drive major forex flows and pricing, while retail traders are a bigger presence in equity trading. Participants therefore differ, with currencies mostly reacting to big player order flow. Stocks are more exposed to both institutional and individual investors.
In summary, forex offers higher liquidity, 24-hour trading, and more leverage, while stocks provide access to company shares in a more restricted market.
Correlation Between Forex and Stock Markets
While distinct markets, forex and stocks share some key similarities. Both involve speculating on the future price of a financial asset, requiring analysis of factors impacting valuations. Traders in both markets aim to profit by buying low and selling high.
Additionally, forex and stocks sometimes trend together, as economic conditions impact currencies and equities alike. For example, strong GDP and employment growth tends to lift stocks and strengthen a country’s currency. Conversely, recessions may cause both equities and currencies to decline.
Both markets are also driven in part by changes in interest rates and inflation. Rising rates can boost currencies but weigh on stock valuations. Inflation can undermine currency values while boosting hard assets.
Technical analysis looking at price charts and trends is applicable to forex and stocks alike. Common concepts like support, resistance, moving averages, and breakouts apply to both. Fundamental analysis is crucial as well, focused on economic factors for forex and company specifics for stocks.
While distinct assets, forex and stocks exhibit some shared drivers and characteristics. Traders can leverage knowledge between the two markets. Yet their differences allow for diversification. Blending forex and stocks provides a balanced portfolio.
Which is Better: Forex Trading vs Stock Trading?
There is no definitive answer to which market is better, forex or stocks. Each offers distinct advantages that appeal to different trading styles and goals.
- For short-term traders: Forex may be preferable. Its high leverage allows controlling large positions with less capital. Volatility enables fast profits from quick price swings. Technical analysis rules, with fundamentals secondary. Forex’s liquidity facilitates entering and exiting positions rapidly. The 24-hour nature suits active traders worldwide. Overall, forex caters to short-term traders capitalizing on intraday volatility.
- For long-term investors: Stocks may be the better choice. Prices reflect a company’s earnings growth and overall trajectory. Fundamental analysis is key in evaluating a stock’s value. Investors hold positions for months or years to benefit from rising share prices. Dividends provide income along the way. The stock market offers exposure to various sectors and geographies. For those with a buy-and-hold mindset, stocks are likely the superior asset class.
- For diversification: Blending both markets is optimal for diversity. Despite some correlation, forex and stocks behave differently in various scenarios. Spreading exposure smoothes out risk and takes advantage of distinct opportunities. With prudent position sizing and risk management, including both equities and currencies enhances a portfolio’s roundedness.
Conclusion
So forex favors aggressive short-term traders, stocks suit patient investors, and a mixed portfolio maximizes diversification. Many traders opt to include both forex and stocks in their portfolios. Therefore, consider your individual preferences, trading style, and goals in deciding where to focus.
There is merit in both markets—forex for tactical gains, stocks for strategic growth, and a blend for maximizing balance. With proper practice and risk mitigation, either or both markets can be traded successfully. Just be sure to learn the markets, develop a solid trading plan, and manage risk to maximize success in either market.
FAQs
What are the major currency pairs in forex trading?
The major currency pairs are EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, USD/CAD, and AUD/USD. These pairings of major global economic currencies comprise the highest trading volume.
What are some popular stocks for trading?
Some well-known and highly traded stocks are Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Tesla, Nvidia, Bank of America, and Walt Disney Company. Popular stocks have high daily trading volumes and display sizable price movements.
Is trading forex riskier than stocks?
Forex trading carries more risk due to high intraday volatility, extensive leverage that amplifies gains and losses, and the ability to lose more than your account balance. Stock investing when done prudently and for the long term can be less risky.
What is traded more, forex or stocks?
Forex is traded far more than stocks. The forex market has a daily turnover of over $5 trillion, whereas the New York Stock Exchange has a daily trading volume of about $200 billion. The vast size of the forex market is one of its defining features.
Is it easier to make money in forex or stocks?
It is arguably easier to profit in forex trading than stocks in the short term due to the high intraday volatility and extensive use of leverage in forex. However, long-term buy-and-hold stock investing has proven reliable for meeting investment goals for decades















